Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during CPR
ECMO - on the threshold of a modern algorithm ALS.
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is a method that ensures constant maintenance of gas exchange parameters (sufficient oxygen supply and carbon dioxide removal) with the ability to reduce peak inhalation, respiratory volume, respiratory rate, and oxygen fraction in the respiratory tract in patients with artificial ventilation of the lungs. Thus, ECMO literally replaces the function of the lungs, in contrast to artificial ventilation of the lungs, and reduces or even completely alleviates its negative effect on the pulmonary tissue.
The first successful case of the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in an adult patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome was presented by Hill and co-inventors in 1972. And in 1976 Bartlett and co-defendants presented the first case when the newborn survived due to the use of ECMO.
Indications for conducting ECMO in adult patients are modified "immediate" and "delayed" criteria were included in the ECMO study conducted in the United States:
- "Immediate" testimony - PaO2?50 mm Hg more than 2 hours at FiO2 = 100; PEEP ?5 cm water;
- "Deferred" testimony - PaO2?50 mm Hg more than 12 hours at FiO2 = 60; PEEP ?5 cm water;
- the ineffectiveness of maximal intensive care for 48 hours.
(FiO2 - oxygen fraction in the inhaled mixture, PaO2- partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood, PEER - positive pressure at the end of expiration).
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during CPR (simulation)
One of the techniques - low-current venous-venous (ESV) ECMO is performed as follows: using two catheters, one of which is implanted in the lower vena cava, a blood sample is passed through the oxygenator (a device where the blood is saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide is removed) , but oxygenated (oxygen saturated) blood returns to the upper vena cava through a catheter that is installed in the right jaw vein. Oxygen is passed through pure oxygen, the gas flow is set according to the target value of the pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood. Oxygenation is carried out both through the own lungs, and with the help of an oxygenator (or exclusively by an oxygenator). The described technique is one of the variants of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, the extracorporeal contour can be used in other modifications.
Arterio-arterial (AA) ECMO is shown on the video. The catheter with oxygen-enriched blood is set close to the aortic valve through the femoral artery.
Often, the need for such treatment occurs in patients with severe pneumonia (pulmonary inflammation), acute lung damage (for example, due to artificial ventilation or with combined kidney and lung lesions, etc.). In acute respiratory distress syndrome in case of ineffectiveness of the maximum applied traditional therapy for 2-day shows ECMO therapy. In the absence of the need to replace the function of the heart, the more secure method is considered to be the VB ECMO. If necessary, the simultaneous support of the function of the heart (or its replacement) and the function of the lungs is used by the vino-arterial (VA) ECMO or extracorporeal support of life.
Schematic representation of the extracorporeal contour at ECMO
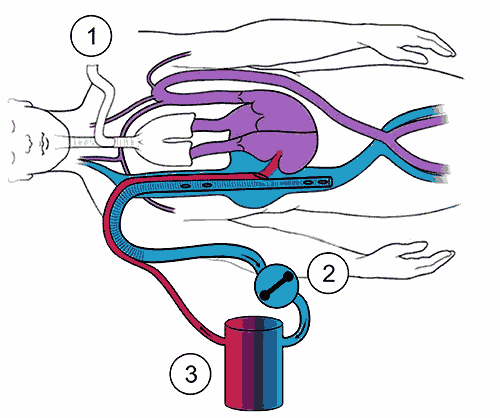
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
(1) - Apparatus for artificial ventilation of the lungs
(2) - Oxygenators
(3) - Roller pump
Since ECMO supports the liveliness of the patient's body to restore lung function, that is, it gives time to wait for the effect of treatment, clear reasons for the popularity of this method in leading clinics in the world. The frequency of the ECMO, which provides for the survival of about 60% of virtually unreliable patients, increases every year (in 2014 ECMO was conducted for approximately 1,000 patients per year, which is more than 10 times more than in 2008).
The availability of modern equipment and the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for the treatment of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, postkarodiotomicheskim syndrome and severe otogeny and hospital pneumonia can hope for a successful treatment of even such serious and dangerous diseases.
The material is provided to healthcare professionals. Not for commercial use. When copying and publishing on other resources, an active reference to this article is required.
I liked the material - do not forget to put a word and subscribe to YouTube channel.